Sloth Bear Introduction
Melursus ursinus (literal meaning: honey bear)
The Sloth Bear is a medium-sized bear native to the Indian subcontinent. They have long snouts and lips, are lankier than other bears and have thick shaggy fur. There are two subspecies – the Indian Sloth Bear and the Sri Lankan Sloth Bear.
Indian Sloth Bear
This is the larger subspecies and has a bigger skull than the Sri Lankan Sloth Bear. It is the most common bear type in India and lives in the forested areas bordering the outer range of the Himalayas as well as parts of Nepal.
Sri Lankan Sloth Bear
The Sri Lankan Sloth Bear is smaller than its Indian cousin and has much shorter body fur and sometimes lacks the characteristic white chest markings. This species is restricted to the northern and eastern lowlands of Sri Lanka.
Sloth Bear Size
Sloth bears on average weigh 90 to 140 Kg, grow to 2 metres in length and up to 1 metre tall at the shoulder. Like most bears, males are larger than females, growing to between 80 and 140 Kg with females reaching 55 to 95 Kg. They are not big bears and are less than half the size of grizzly bears, which can often reach 270 Kg.
Sloth Bear Lifespan
In captivity Sloth, Bears can live up to 40 years but in the wild, it is usually 20 to 25 years.
Sloth Bear Speed
Generally, sloth bears move in a slow and lazy manner but they can gallop at speed if they need to and move much faster than humans if necessary.
Sloth Bear Habitat
Sloth bears inhabit forest and grassland areas around the base of the Himalayas. Their current range includes India from Punjab to Arunachal Pradesh, Southern Nepal and Sri Lanka. They once inhabited Bangladesh and Bhutan too but it is thought they may be extinct from these areas now. I have indicated on the map below the rough area that Sloth bears are thought to inhabit.
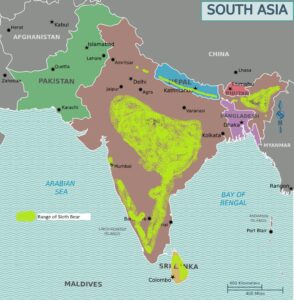
Sloth Bear Reproduction
The Sloth Bear breeding season changes depending on location. In Sri Lanka, it lasts all year but in India, they mate in April, May and June and give birth in winter with a gestation period of 6 to 7 months. Like most bears, they give birth to blind, hairless and helpless babies but unlike other bears, these babies develop quite quickly and the cubs can start walking a month after birth.
The mother will typically give birth to one or two cubs (on rare occasions she might give birth to three) and will usually remain in the cave with them for 8 to 10 weeks. When they are ready to emerge, the cubs will travel around on the back of their mothers and will continue to travel in this way for up to six months.

Sloth Bear Diet
Sloth bears predominantly eat termites. Outside of the fruiting season, insects make up around 95% of their diet. During the monsoon season, when the trees are fruiting they will eat figs, mangos, jack fruit and the pods of the Cassia tree. In March and April, they will eat the fallen flowers of the Mowha tree.
Sloth bears also love honey. They will climb trees to knock down the honeycomb on to the floor where they can eat it. They will sometimes ear carrion to supplement their diet but do not hunt other animals (apart from insects). They may sometimes raid crops and are particularly partial to sugar cane.
Sloth Bear Adaptations
Sloth bears have a number of adaptations that help them in their tropical habitats and with their diets of predominantly insects. Although shaggy and looking thick, their fur lacks an undercoat to keep them relatively cool. They have a good sense of smell and their nostrils can close completely which helps when they are raiding ant and termite nests, and their claws are ideally suited to digging out termites from their nests. Additionally, they are missing their front two teeth and have very long tongues which enables them to suck up termites with ease. Their molars are smaller than other bears but they retain their large canine teeth for use in defence. Finally, their feet are turned inwards to assist with digging.

Sloth Bear Predators
Besides humans, sloth bears do have some natural predators. Tigers are the main danger. Sloth bears have big, sharp teeth and can be somewhat aggressive so most tigers will avoid them but there are reports of tigers lying in wait for the bears near termite mounds and sloth bear fur has been found in tiger scat. Leopards can also be a threat. They are unlikely to attack healthy adult bears but can and will attack young bears. They are a particular threat as they can chase the bears up trees.
Interestingly, although they do not predate the bears, elephants and rhinos do not tolerate the bears in their vicinity and will chase them down. The same animals are known to tolerate tigers so it is unknown as to why this is the case. Sloth bears coexist peacefully with both Asiatic Black Bears and Sun Bears.
Are Sloth Bears Dangerous?
Sloth bears are one of the smaller bear species and they eat insects and fruit but they are actually (per capita) the most dangerous bear species in the world and are responsible for around 12 deaths each year and maul many more. This is twice as many as the much larger brown bears who are far more numerous.
So, why are Sloth Bears so dangerous? Well, one obvious answer is that they are more and more likely to come into contact with humans. India is one of the most populous countries in the world and people are encroaching ever further onto the bear’s habitat. Compare this to the polar bear, for example, and it is easy to see how they are more likely to be in a position to attack.
It is important to point out that sloth bears are not attacking humans eat or because they are aggressive, they are doing it to defend themselves from a perceived threat. One theory is that unlike many other bears, sloth bears regularly come into contact with a skilled and powerful predator – the Bengal Tiger. In order to survive, the bears must be able to defend themselves. They do not bluff attack, like a larger brown bear might, and just launch straight into a real defence with sometimes fatal consequences.
In order to avoid an attack, it is important to make as much noise as possible. These bears would much rather avoid humans if possible, with most attacks occurring because they are startled and surprised.
Are Sloth bears endangered?
Sloth bears are classed as vulnerable, one step down from endangered and there are thought to be less than 20,000 of these bears left in the wild. The reasons for their vulnerability are sadly very familiar. Their habitat has been reduced by human activities and people often kill the bears. In the past, they have been hunted for their gall bladders and for use in entertainment shows. The good news is that their trade has been banned by the Indian government but they are still killed by humans as they can destroy crops and may be dangerous to people.
Their numbers are not recovering, unlike for the more charismatic large mammals such as tigers and elephants but they have stabilised in areas where tiger conservation is ongoing, suggesting that these efforts to protect tiger habitats also help the sloth bears.

Sloth Bears in Culture
Probably the most famous fictional sloth bear is Baloo from Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book. In the book, Baloo is a sleepy old bear who teaches the law of the jungle to Mowgli. Although brown bears and black bears are present in India, the sloth bear is the only species present in the Seoni area where the novel takes place and Baloo’s cuisine consists of roots, nuts and honey which is a good fit with the Sloth bear.
FAQs
Why are they called Sloth Bears?
The bear was named by European zoologist George Shaw. When he saw the bears had long claws, unusual teeth and occasionally hung upside down on tree branches, he assumed they were related to sloths and thus gave them their name.
Can a Sloth Bear kill a tiger?
While sloth bears can defend themselves well against tiger attacks, with their sharp teeth and long claws there have been no records of a sloth bear killing a tiger. Tigers will often kill and eat the bears, however.
Do Sloth bears attack humans?
Yes, if they are startled or provoked. Sloth bears are statistically the most dangerous bear species in the world and can launch ferocious attacks with their sharp teeth and claws.
Where do Sloth Bears live?
They live in the forests and grassland in many parts of India and Northern Sri Lanka.
How many Sloth Bears are left in the world?
There are thought to be less than 30,000 left in the wild.
What eats a sloth bear?
Apart from humans, tigers are the bears’ main threat, although leopards can kill and eat young bears.
Can Sloth Bears climb?
Yes, they can climb quite well in order to find food or escape from danger.
